Oppida and online education... I have always been an educator. It’s in my blood. However, over the...
Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality in elearning
Innovation and technology are not just going to shape our future; they will also deeply impact how our next generations educate and shape themselves. Market predictions propose that the global Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), and Mixed Reality (MR) market will reach 30.7 billion U.S. dollars by the end of 2021. Those same predictions forecast an increase to 300 billion U.S. dollars by 2024. So, there is money in future tech; not a huge surprise—though 877% growth in 3 years is jaw dropping, to say the least. What is more interesting is that Extended Reality (XR) industry experts are betting on virtual reality and augmented reality in elearning and education as the leading industry for their use case application.
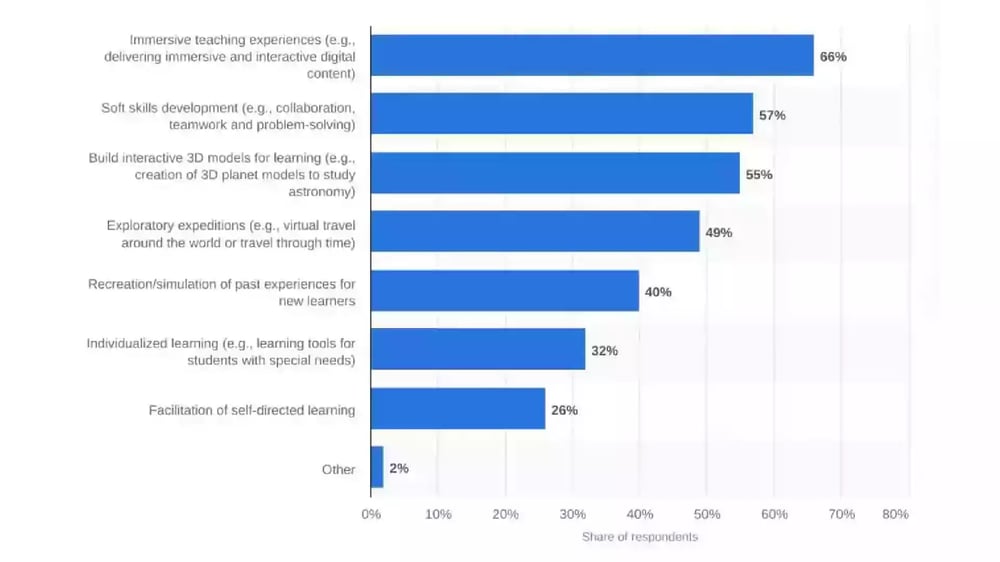
So what do those use cases in education look like? What are the applications of VR and AR? First, a comparative definition to set the stage for our discussion.
Extended Reality (XR), Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)—what is the difference?
XR is an emerging umbrella term that covers future and immersive technologies, including the ones we already have available today: AR, VR, and (MR) plus those that are yet to be created. These immersive technologies extend the reality we experience by either combining the virtual and “real” world or by simulating a fully immersive experience. For instance, VR and AR’s core difference is that VR puts you into the computer’s world, whereas AR is about pulling the computer into our world.
With Augmented Reality, students enter a virtual, three-dimensional environment filled with rich online content that digitally conveys the sights, sounds and even the dangers of a seemingly real-life situation without losing contact with students’ surroundings. Pokemon Go is a great gamified example of this.
In contrast, Virtual Reality fully engrosses students in a simulated activity that shuts the rest of the world out. Instead of the student interacting with a very real piece of machinery or a real-life situation, imaginary equipment or scenarios spring up through VR glasses or a VR headset, so everything the student sees is a simulation—making it much more like an interactive movie.

XR tech: the pros and cons
The pros
Future technologies open up new learning environments and possibilities. Here are just a few of the pros of XR tech application in education:
- Educators and students can get together in the same room through digital representations of themselves—instructors and trainers can join students in the online simulation and guide students through their experiences—from wherever both parties are in the world.
- Since VR provides full simulations and AR provides lifelike setups with faults built into the system, both technologies offer learning experiences that can mimic real-world situations to a degree not possible with traditional teaching methods. If students were to engage with an extended technology sequence improperly, they would see the ‘real’ consequences of their actions and better understand what happens when they don’t follow proper procedures.
- Consider the use case scope: architecture and design, virtual field trips, immersion, skills and machinery training, philosophical theories, distance and game-based learning, and collaboration possibilities, to name just a few.
- There are also comprehensive application possibilities across various industries: aerospace, healthcare, transport, computing, public services, construction, manufacturing, pharmaceutical, agriculture, etc.
- A key benefit of these techs is the inherent ability to be able to collect powerful metrics not typically available through in-person training scenarios such as timing, body movements, decision making aptitude, and more.
- Future technologies unlock new possibilities, enhance existing practices and allow for unique methodologies and techniques to be implemented.
- Students can practise real-world skills in a simulated environment without injuring themselves while at the same time learning through game-like devices that add interaction and fun.
- Future-ready institutions could potentially send full brick-and-mortar lab facilities via VR or AR to remote/international locations.
- XR tech has the potential to help bridge the skills gap between education and industry.
- Graduate candidates leave training and education paths with more experience and confidence, increasing their speed to full competence when starting new careers.

The cons
- Complex technology is costly technology. The investment for XR tech needs to cover training for instructors/teachers, learning and curriculum designers, and technology specialists to collaborate on developing course material with augmented, virtual and mixed-reality features, which is why AR and VR are often considered expensive afterthoughts.
- Potential privacy and confidentiality issues surrounding the tech, its usage, the content development process, and more.
- Some people experience physical side effects when using these techs including motion sickness, headaches, nausea, and eyestrain.
- Additional accessibility and inclusivity barriers to entries and the possibility of creating more inequality in education: for example, for people with disabilities, the expense of such tech, device accessibility and availability, increased technical and connectivity issues, etc.
- In our desire to expand the scope of learning environments, it is important that adding more technology into the mix does not devalue the importance of human connection in education and the everyday world.
- As with anything new, these future technologies are already facing resistance in education. Those with inflexible mindsets who are not yet ready for the future of digital and blended learning are also opposed to the idea that XR tech could be beneficial in enhancing pedagogy. The unique nature of learning approaches required for XR technology are very different from the common delivery-based and teacher-centered approach that many institutions still favour.

Conclusion
The events of 2020 created a sense of urgency that has accelerated the digital transformation of training and education worldwide. With more industries and institutions adopting remote learning and work approaches in the future, XR tech has the potential to expand the scope of education to limits perhaps set only by our imaginations. Yet, the costs set very real limitations for many institutions right now which do not have the funds to hire a dedicated company to help them produce XR tech content.
At Oppida, we believe in raising the bar in online learning design and we have little doubt about these future technologies being part of the next generation of education. We will be working to overcome the pedagogical challenges linked to these techs with institutions, educators, and companies interested in implementing this technology. Oppida is keen to explore learning design solutions for the XR tech landscape in collaboration with like-minded, forward-thinking partners.




